Access a range of climate-related reports issued by government agencies and scientific organizations. Browse the reports listed below, or filter by scope, content, or focus in the boxes above. To expand your results, click the Clear Filters link.
This is the FY22 edition of the U.S. Gllobal Change Research Program's annual report to Congress mandated by the the Global Change Research Act. The report provides an overview of the Program’s progress in delivering on its strategic goals as well as a summary of agency expenditures under USGCRP’s budget crosscut.
Hotter weather, stronger typhoons, coral reef death, and physical and mental health risks are among the major challenges detailed in this report on climate change in the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI). Threatened resources include high-value coastal infrastructure and the millions of dollars that ocean ecosystems add to the CNMI economy annually. This report provides guidance for decision makers seeking to better understand the implications of climate variability and change for CNMI and its communities and identifies the additional information and research needed to support responses that enhance resilience and help CNMI to withstand the changes to come.
Planning for climate change resiliency is an increasingly pressing requirement for communities throughout the world and the Delaware Valley Regional Planning Commission (DVRPC) region. In order to help local officials, non-profits, and communities with this process, numerous planning tools have been developed by a wide range of public and private agencies. Accordingly, the purpose of this paper is to explain, organize, and prioritize the tools that currently exist in order to select ones that are broadly accessible to a wide range of organizations, applicable across a range of sectors, and not overly redundant. During this selection process, a list of over 60 tools was winnowed down to a final toolkit of 18 that are particularly useful at any stage in the resiliency planning process and can be used for communities throughout the DVRPC region.
As higher seas, stronger storms, and more frequent flooding collide with COVID-19, communities of every size across the United States must address new challenges emerging from overlapping disasters. This handbook is a comprehensive resource to help local officials and emergency managers address the dual disaster scenario of flooding during the COVID-19 pandemic. This handbook, the first of its kind, draws on case studies and best practices from emergency management professionals to equip officials with six actionable recommendations for planning a proactive response as communities face multiple threats this season.
In the third quarter of 2017, Hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria revealed some significant vulnerabilities in the national and regional supply chains of Texas, Florida, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Puerto Rico. Drawing on lessons learned during the 2017 hurricanes, this report explores future strategies to improve supply chain management in disaster situations. It makes recommendations to strengthen the roles of continuity planning, partnerships between civic leaders with small businesses, and infrastructure investment to ensure that essential supply chains will remain operational in the next major disaster. Focusing on the supply chains food, fuel, water, pharmaceutical, and medical supplies, the recommendations of this report will assist FEMA as well as state and local officials, private sector decision makers, civic leaders, and others who can help ensure that supply chains remain robust and resilient in the face of natural disasters.
The Beloved Community is a vision for our future where all people share equally in the wealth and bounty of the earth, where we protect its abundance, diversity, and beauty for future generations. In this vision of liberation, racism, exploitation, and domination are replaced by democracy, cooperation, interdependence, and love. To get there, we pursue transformative, systems-change solutions. What do we mean by this? The root causes of the problems our communities face—like climate change, racism, and economic inequality—are all deeply connected. Since the problems are connected, so are the solutions. The purpose of this toolkit is to put us on the path toward achieving this vision. Through the context of building equity and resilience into climate adaptation planning, we introduce strategies to transform our communities and, by extension, society. Our ultimate goal is to create lasting and systemic change. At the same time, we recognize the urgency of the issues our communities face and the need to take action now. That is why we pursue change at every scale—from policy changes to community-based projects—to institute the transformative change we need to uphold our vision of the beloved community.
The Tampa Bay region is known as one of the most vulnerable in the world to wind damage, coastal flooding from storm surge, and rising sea levels. The City of St. Petersburg—with over 60 miles of coastal frontage—has already felt the impacts of storms. The adverse effects from these types of environmental events often impact low-income communities the hardest, as they have the most difficulty bouncing back from stresses and shocks. The City of St. Petersburg is committed to ensuring that investments in making the city resilient are equitable and create a range of opportunities that everyone can benefit from. The Urban Land Institute of Tampa Bay convened top experts in climate resilience from New Orleans, Miami, Boston, and the Tampa Bay region to provide technical assistance to the city on creating an equitable culture of resilience. A grant from the ULI Foundation and Kresge Foundation funded this effort.
This guidebook results from the culmination of a year of dialogue among diverse stakeholders in southeastern Connecticut who defined challenges and solutions from extreme weather, climate change, and shifting social and economic conditions. Participants included representatives from nine municipalities, public and private utilities, public health departments, chambers of commerce, major employers, conservation organizations, academic institutions, community non-profits, and state agencies, among others. The dialogue captured six themed planning sectors (water, food, ecosystem services, transportation, energy, and regional economy) in a process that used surface and integrated solutions to address singular and multiple challenges across planning sectors. The guidebook provides a quick reference resource to help shape and inform actions that will advance a regional resilience framework for southeastern Connecticut; an accompanying Summary of Findings captures the project's final outcomes and conclusions, as well as providing a comprehensive account of the objectives, process, and details.
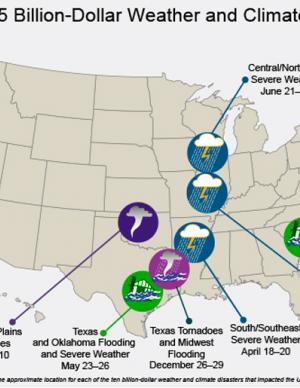
The National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) is the nation's scorekeeper in terms of addressing severe weather and climate events in their historical perspective. As part of its responsibility of monitoring and assessing the climate, NCEI tracks and evaluates climate events in the U.S. and globally that have great economic and societal impacts. Found on these webpages are information on the weather and climate events that have had the greatest economic impact from 1980 to 2015. The U.S. has sustained 188 weather and climate disasters since 1980 where overall damages/costs reached or exceeded $1 billion (including CPI adjustment to 2015). The total cost of these 188 events exceeds $1 trillion.
Coastal communities across the United States are facing worsening risks of flooding during routine high tides and damaging storm surges. With sea level rise accelerating along the East and Gulf Coasts, these problems are projected to intensify in the coming years, and they are likely to have a disproportionate impact on low-income and minority communities. This report is an attempt to guide improvements in policy making around disaster aid and preparedness, to ensure that communities receive the support they need before and in the aftermath of climate-related disasters. It also makes the case for better long-term planning and sufficient resources to anticipate and prioritize the needs of frontline communities who bear the brunt of the climate impacts our nation is experiencing.
This guide offers a collection of 19 practical strategies for building owners to make their properties more resilient against the effects of extreme weather events. It draws on advice from over 50 experts in the field of resilience as well as the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) and the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP). In addition, the manual offers guidance on determining a property’s vulnerability to various hazards, finding which strategies are relevant to a particular building, and getting started with a resilience plan.
This report—the first phase of the Department of the Interior (DOI) assessment effort for Hurricane Sandy projects—was developed for DOI by a metrics expert group of physical and ecological scientists and socioeconomic experts who recommended performance metrics for measuring changes in resilience resulting from the DOI-sponsored projects. It identifies natural and artificial coastal features most affected by Hurricane Sandy along the Northeast coast—such as marshes, beaches, and estuaries—and recommended metrics that would indicate resilience change in those features.
This report details the results of a two-year study to address coastal storm and flood risk to vulnerable populations, property, ecosystems, and infrastructure affected by Hurricane Sandy in the United States' North Atlantic region. The study was designed to help local communities better understand changing flood risks associated with climate change and to provide tools to help those communities better prepare for future flood risks. It builds on lessons learned from Hurricane Sandy and attempts to bring to bear the latest scientific information available for state, local, and tribal planners.
The American Planning Association's Hazards Planning Center worked with FEMA to develop Planning for Post-Disaster Recovery: Next Generation. This updated manual offers a no-nonsense explanation of the benefits and limitations of planning for unpredictable events.
This report outlines 100 recommendations to help improve federal programs and their ability to prepare for climate change, drawing from a series of workshops with leading federal, state, and local officials and building upon lessons learned post-disaster in New Orleans (following Hurricane Katrina), New York (following Hurricane Sandy), and Vermont (after Hurricane Irene). The report identifies more than 30 federal programs, initiatives, and laws that can be used to prepare for extreme events such as storms, floods, and heat waves as well as rising seas. This report informed the White House's State, Local, and Tribal Leaders Task Force on Climate Preparedness and Resilience.
This update serves as guidance for hazard mitigation for the State of Connecticut. Its vision is supported by three central goals, each with an objective, a set of strategies, and associated actions for Connecticut state government, stakeholders, and organizations that will reduce or prevent injury from natural hazards to people, property, infrastructure, and critical state facilities.
PlaNYC is a long-term sustainability plan based on the latest climate science. This report includes ideas on how to rebuild the communities in New York City affected by Hurricane Sandy in 2012 and how to increase resilience and infrastructure of buildings city-wide in order to protect against future extreme events.
No person or place is immune from disasters or disaster-related losses. Infectious disease outbreaks, acts of terrorism, social unrest, or financial disasters in addition to natural hazards can all lead to large-scale consequences for the nation and its communities. Communities and the nation thus face difficult fiscal, social, cultural, and environmental choices about the best ways to ensure basic security and quality of life against hazards, deliberate attacks, and disasters. Beyond the unquantifiable costs of injury and loss of life from disasters, statistics for 2011 alone indicate economic damages from natural disasters in the United States exceeded $55 billion, with 14 events costing more than a billion dollars in damages each.
One way to reduce the impacts of disasters on the nation and its communities is to invest in enhancing resilience--the ability to prepare and plan for, absorb, recover from and more successfully adapt to adverse events. Disaster Resilience: A National Imperative addresses the broad issue of increasing the nation's resilience to disasters. This book defines "national resilience", describes the state of knowledge about resilience to hazards and disasters, and frames the main issues related to increasing resilience in the United States. It also provide goals, baseline conditions, or performance metrics for national resilience and outlines additional information, data, gaps, and/or obstacles that need to be addressed to increase the nation's resilience to disasters. Additionally, the book's authoring committee makes recommendations about the necessary approaches to elevate national resilience to disasters in the United States.
Enhanced resilience allows better anticipation of disasters and better planning to reduce disaster losses-rather than waiting for an event to occur and paying for it afterward. Disaster Resilience confronts the topic of how to increase the nation's resilience to disasters through a vision of the characteristics of a resilient nation in the year 2030. Increasing disaster resilience is an imperative that requires the collective will of the nation and its communities. Although disasters will continue to occur, actions that move the nation from reactive approaches to disasters to a proactive stance where communities actively engage in enhancing resilience will reduce many of the broad societal and economic burdens that disasters can cause
This plan identifies Ohio's mitigation strategy, which helps guide local mitigation planning and project efforts. The State of Ohio Standard Hazard Mitigation Plan was first approved by FEMA in 2005. This 2011 plan revision details Ohio’s highest priority hazards: river/stream flooding, tornadoes, winter storms, landslides, dam/levee failure, wildfire, coastal flooding, earthquakes, coastal erosion, drought, severe summer storms, invasive species, and land subsidence hazards. The plan also integrates and introduces the State Hazard Analysis, Resource and Planning Portal (SHARPP), a web-based system that captures and disseminates state and local hazard mitigation planning and project information.
This report is designed to help Oregon's local decision makers prepare adaptation plans and state agencies to coordinate their infrastructure plans with local adaptation initiatives.
This report summarizes findings from a review of coastal hazards associated with sea level rise, hurricanes, nor'easters, and reduced sediment supply. The study also evaluates existing policies and potential knowledge gaps, and develops potential adaptation policies.