Access a range of climate-related reports issued by government agencies and scientific organizations. Browse the reports listed below, or filter by scope, content, or focus in the boxes above. To expand your results, click the Clear Filters link.
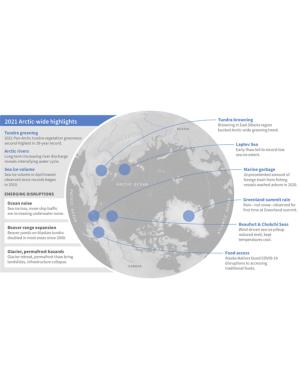
As the influences of human-caused global warming continue to intensify, with the Arctic warming significantly faster than the globe overall, the 2021 Arctic Report Card (ARC2021) brings a broad view of the state of the Arctic climate and environment. The ARC2021 provides an update on seven Arctic Vital Signs, from sea ice to snow and air temperatures to tundra greenness, and checks in on three Indicator topics for updates on river discharge, ocean acidification, and observations of substantial Arctic beaver expansion. The noteworthy emerging topics in the four ARC2021 Frostbites—marine debris, marine noise, food access during the COVID-19 pandemic, and glacier and permafrost hazards—share a common link as they look at the impacts of more people and human activity in the Arctic as well as the challenges and hazards people face with the rapidly changing cryosphere. The scientific and observational story of the Arctic is a human story—of climate change, of increased shipping and industrial activity, and of communities responding to local and regional disruptions.
The Working Group II contribution to the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report assesses the impacts of climate change, looking at ecosystems, biodiversity, and human communities at global and regional levels. It also reviews vulnerabilities and the capacities and limits of the natural world and human societies to adapt to climate change.
The Vermont Climate Action Plan aims to dramatically reduce greenhouse gas emissions, help protect Vermont communities and landscapes from the greatest risks of climate change, and create new clean energy industry and jobs. The Climate Action Plan includes strategies to:
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation, building, regulated utility, industrial, commercial, and agricultural sectors;
- Encourage smart growth and related strategies;
- Achieve long-term sequestration and storage of carbon and promote best management practices to achieve climate mitigation, adaption, and resilience on natural working lands;
- Achieve net zero emissions by 2050 across all sectors;
- Reduce energy burdens for rural and marginalized communities;
- Limit the use of chemicals, substances, or products that contribute to climate change; and
- Build and encourage climate adaptation and resilience of Vermont communities and natural systems.
The Climate Action Plan serves as a guide for the Vermont Legislature in setting policy that supports climate change solutions for Vermonters and Vermont's landscape.
A range of resources documenting report preparation are available in the Climate Action Plan Appendices.
In 2020, New York City's Mayor’s Office of Resiliency initiated an engagement process, called the Climate Knowledge Exchange, to align research with climate resiliency and adaptation needs. This report is the first in an annual series that will maintain a public agenda for climate research in NYC. The report communicates NYC’s research needs to external partners, including academic scientists, federal researchers, philanthropic foundations, and community organizations. This in turn will catalyze new and creative partnerships to develop credible and actionable research products that address NYC’s most pressing climate challenges. The report includes the engagement methodology and survey text used with various agencies.
The heavy precipitation and flooding of 2019 was one for the history books. This report looks back at the major climate events and impacts of 2019 in the Missouri River Basin.
As the world strives to cut greenhouse gas emissions and limit climate change, it is crucial to track progress towards globally agreed climate goals. For a decade, the Emissions Gap Report has compared where greenhouse gas emissions are heading against where they need to be, and highlighted the best ways to close the gap. This report presents the latest data on the expected gap in 2030 for the 1.5°C and 2°C temperature targets of the Paris Agreement. It considers different scenarios, from no new climate policies since 2005 to full implementation of all national commitments under the Paris Agreement. For the first time, it looks at how large annual cuts would need to be from 2020 to 2030 to stay on track to meeting the Paris goals. The report looks at the potential of the energy transition—particularly in the power, transport, and buildings sectors—and efficiency in the use of materials such as iron steel and cement.
The Beloved Community is a vision for our future where all people share equally in the wealth and bounty of the earth, where we protect its abundance, diversity, and beauty for future generations. In this vision of liberation, racism, exploitation, and domination are replaced by democracy, cooperation, interdependence, and love. To get there, we pursue transformative, systems-change solutions. What do we mean by this? The root causes of the problems our communities face—like climate change, racism, and economic inequality—are all deeply connected. Since the problems are connected, so are the solutions. The purpose of this toolkit is to put us on the path toward achieving this vision. Through the context of building equity and resilience into climate adaptation planning, we introduce strategies to transform our communities and, by extension, society. Our ultimate goal is to create lasting and systemic change. At the same time, we recognize the urgency of the issues our communities face and the need to take action now. That is why we pursue change at every scale—from policy changes to community-based projects—to institute the transformative change we need to uphold our vision of the beloved community.
This plan represents the efforts of the State of Minnesota in fulfilling the responsibility for hazard mitigation planning. The purpose of this plan is to identify the state’s major hazards, assess the vulnerability to those hazards, and take steps to reduce vulnerability using the technical and program resources of Minnesota agencies. The process has included consideration of current and expected future impacts from Minnesota’s already changing climate, as relevant to hazard mitigation planning. The plan identifies goals and recommends actions and initiatives for the state government to adapt to, reduce, and/or prevent injury and damage from hazardous events.
Climate change is causing significant and far-reaching impacts on the Great Lakes and the Great Lakes region. This report, from 18 leading scientists and experts from Midwest and Canadian universities and research institutions, draws on the array of existing research to assess how the shifting global climate impacts the unique Great Lakes region.
The Global Change Research Act of 1990 mandates that the U.S. Global Change Research Program deliver a report to Congress and the President no less than every four years that “1) integrates, evaluates, and interprets the findings of the Program…; 2) analyzes the effects of global change on the natural environment, agriculture, energy production and use, land and water resources, transportation, human health and welfare, human social systems, and biological diversity; and 3) analyzes current trends in global change, both human-induced and natural, and projects major trends for the subsequent 25 to 100 years.” The Fourth National Climate Assessment (NCA4) fulfills that mandate in two volumes. This report, Volume II, draws on the foundational science described in Volume I, the Climate Science Special Report. Volume II focuses on the human welfare, societal, and environmental elements of climate change and variability for 10 regions and 18 national topics, with particular attention paid to observed and projected risks, impacts, consideration of risk reduction, and implications under different mitigation pathways. Where possible, NCA4 Volume II provides examples of actions underway in communities across the United States to reduce the risks associated with climate change, increase resilience, and improve livelihoods. This assessment was written to help inform decision makers, utility and natural resource managers, public health officials, emergency planners, and other stakeholders by providing a thorough examination of the effects of climate change on the United States.
This special report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate change describes the impacts of global warming of 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels. The report also describes potential global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development, and efforts to eradicate poverty.
The Arctic shows no sign of returning to reliably frozen region of recent past decades. Despite relatively cool summer temperatures, observations in 2017 continue to indicate that the Arctic environmental system has reached a "new normal," characterized by long-term losses in the extent and thickness of the sea ice cover, the extent and duration of the winter snow cover and the mass of ice in the Greenland Ice Sheet and Arctic glaciers, and warming sea surface and permafrost temperatures. Issued annually since 2006, the Arctic Report Card is a timely and peer-reviewed source for clear, reliable, and concise environmental information on the current state of different components of the Arctic environmental system relative to historical records. The report is intended for a wide audience, including scientists, teachers, students, decision makers, and the general public interested in the Arctic environment and science.
As a key part of the Fourth National Climate Assessment (NCA4), the U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP) oversaw the production of this stand-alone report of the state of science relating to climate change and its physical impacts. The Climate Science Special Report (CSSR) is designed to be an authoritative assessment of the science of climate change, with a focus on the United States, to serve as the foundation for efforts to assess climate-related risks and inform decision making about responses.
As Volume 1 of NCA4, CSSR serves several purposes, including providing (1) an updated and detailed analysis of the findings of how climate change is affecting weather and climate across the United States; (2) an executive summary and 15 chapters that provide the basis for the discussion of climate science found in the second volume of NCA4; and (3) foundational information and projections for climate change, including extremes, to improve “end-to-end” consistency in sectoral, regional, and resilience analyses within the second volume. CSSR integrates and evaluates the findings on climate science and discusses the uncertainties associated with these findings. It analyzes current trends in climate change, both human-induced and natural, and projects major trends to the end of this century. As an assessment and analysis of the science, CSSR provides important input to the development of other parts of NCA4, and their primary focus on the human welfare, societal, economic and environmental elements of climate change. Much of the underlying report is written at a level more appropriate for a scientific audience, though the Executive Summary is intended to be accessible to a broader audience.
This guidebook results from the culmination of a year of dialogue among diverse stakeholders in southeastern Connecticut who defined challenges and solutions from extreme weather, climate change, and shifting social and economic conditions. Participants included representatives from nine municipalities, public and private utilities, public health departments, chambers of commerce, major employers, conservation organizations, academic institutions, community non-profits, and state agencies, among others. The dialogue captured six themed planning sectors (water, food, ecosystem services, transportation, energy, and regional economy) in a process that used surface and integrated solutions to address singular and multiple challenges across planning sectors. The guidebook provides a quick reference resource to help shape and inform actions that will advance a regional resilience framework for southeastern Connecticut; an accompanying Summary of Findings captures the project's final outcomes and conclusions, as well as providing a comprehensive account of the objectives, process, and details.
New U.S. regional sea level scenarios developed by NOAA and its partners will give coastal communities better, more localized data to help them plan for and adapt to the risk of rising sea levels to their economies and infrastructure.
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB), in collaboration with the Council of Economic Advisers (CEA), has attempted to quantify the fiscal risks posed by climate change for the Federal Government. To date, this effort has yielded two primary conclusions: first, that our current understanding of the fiscal risks of climate change is nascent, limited in scope, and subject to significant uncertainty; and second, that the evidence available thus far indicates the fiscal risks to the Federal Government could be very significant over the course of this century without ambitious action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) and adapt our communities to a changing climate.
This report outlines the contours of fiscal risk through five program-specific assessments: crop insurance, health care, wildfire suppression, hurricane-related disaster relief, and Federal facility flood risk. These programs were assessed because they are directly influenced by climate change, they have strong links to the Federal Budget, and quantitative scientific and economic models regarding the likely magnitude of impacts were available. This report also considers potential impacts to Federal revenues.
This report documents that the average temperature in 2015 was over one degree higher than pre-industrial times and that the period 2011–2015 was the warmest five-year period on record, consistent with established warming trends. The report further documents that in 2015 another milestone was reached, with globally averaged CO2 levels of 400 parts per million (ppm). The year 2016 is on track to be even warmer and will be the first year in which CO2 at the Mauna Loa Observatory remains above 400 ppm all year, and for many generations to come.
The probability of extreme climate events since 2011, especially those involving extreme high temperatures, has been substantially increased by climate change, often by a factor of 10 or more. The single most significant event in humanitarian terms, with over 250,000 lives lost, was the 2011–2012 famine in the Horn of Africa, where drought was a major factor.
With insight from 26 campus and stakeholder advisors, the support of the USDA Agricultural Marketing Service’s Transportation Division, and input from regional food supply chain businesses throughout the region, this 68-page report details the process used to assess the Chicago region food system and findings through the three-year participatory research effort. It includes eleven sections with 17 figures to illustrate key concepts, along with extensive supporting materials. The report presents three innovations with proofs of concept that could be applied widely in the region and beyond to improve food distribution, both in rural and urban regions.
This Web toolkit raises airport operator awareness about vulnerabilities caused by significant weather events. The toolkit helps airports develop more robust contingency and recovery plans, in addition to their airport emergency plans. The toolkit focuses on events that are “rare but plausible”; that is, events that may have happened in the distant past, or in adjacent geographic areas, but are not common event types at the airport itself, and therefore may not be in the forefront of the airport managers’ minds.
This report features observed trend data on 37 climate indicators, including U.S and global temperatures, ocean acidity, sea level, river flooding, droughts, and wildfires. It documents rising temperatures, shifting patterns of snow and rainfall, and increasing numbers of extreme climate events, such as heavy rainstorms and record high temperatures. Many of these observed changes are linked to the rising levels of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in our atmosphere, caused by human activities.
This document provides final guidance for federal agencies on how to consider the impacts of their actions on global climate change in their National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) reviews, providing a framework for agencies to consider both the effects of a proposed action on climate change, as indicated by its estimated greenhouse gas emissions, and the effects of climate change on a proposed action. The memorandum applies to all types of proposed federal agency actions that are subject to NEPA analysis and guides agencies on how to address the greenhouse gas emissions from federal actions and the effects of climate change on their proposed actions within the existing NEPA regulatory framework.
The State of Maine is experiencing shifts in atmospheric and oceanographic conditions that put it at the precipice of abrupt climate change. This report—part of the Department of Homeland Security's Regional Resiliency Assessment Program (RRAP)—focuses on the local and regional consequences of climate disruptions and their impacts on critical infrastructure in the Casco Bay region, the most developed and populous region in Maine. The report identifies vulnerabilities that may potentially affect the region’s ability to maintain its critical infrastructure systems and recover from the impacts of climate change.
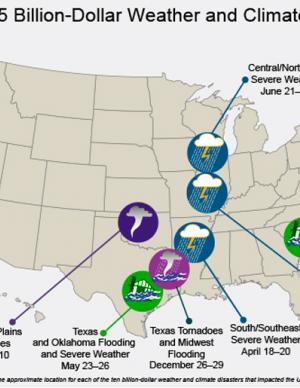
The National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) is the nation's scorekeeper in terms of addressing severe weather and climate events in their historical perspective. As part of its responsibility of monitoring and assessing the climate, NCEI tracks and evaluates climate events in the U.S. and globally that have great economic and societal impacts. Found on these webpages are information on the weather and climate events that have had the greatest economic impact from 1980 to 2015. The U.S. has sustained 188 weather and climate disasters since 1980 where overall damages/costs reached or exceeded $1 billion (including CPI adjustment to 2015). The total cost of these 188 events exceeds $1 trillion.
The 2015 World Economic Forum rated food crises, extreme weather, and failure of infrastructure as top global risks in 2015. Around the world, regions are contending with extreme weather, including drought, flooding, and changes in growing seasons. These extremes affect crops and pests, and may disrupt agriculture and its supply chains, especially in the second half of this century. This paper presents an example of how transportation of agricultural products in the Upper Mississippi River Valley region of the United States may be impacted by, and respond to, a changing climate.
Many climate-related hydrologic variables in New England have changed in the past century, and many are expected to change during the next century. It is important to understand and monitor these changes because they can affect human water supply, hydroelectric power generation, transportation infrastructure, and stream and riparian ecology. This report describes a framework for hydrologic monitoring in New England by means of a climate-response network.
The two main objectives of this pilot project were to (1) assess the vulnerability of Boston's Central Artery/Tunnel System to sea level rise and extreme storm events, and (2) investigate and present adaptation options to reduce identified vulnerabilities.
Successfully negotiating climate change challenges will require integrating a sound scientific basis for climate preparedness into local planning, resource management, infrastructure, and public health, as well as introducing new strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions or increase carbon sequestration into nearly every sector of California’s economy. This Research Plan presents a strategy for developing the requisite knowledge through a targeted body of policy-relevant, California-specific research over three to five years (from early 2014), and determines California’s most critical climate-related research gaps.
This report builds on Maine’s earlier report from 2009—it is not intended as a comprehensive revision of all aspects of the original report. This update focuses on highlights of the understanding in 2015 of past, present, and future trends in key indicators of a changing climate specific to Maine, and recent examples of how Maine people are experiencing these changes.
This report provides current and relevant climate adaptation information to a diverse audience of legislators, government agencies, policy makers, educators, nongovernment organizations, business, industry, researchers, other stakeholders and the public.
A 24-year tradition encompassing the work of 425 authors from 57 countries, 2013's State of the Climate report uses dozens of climate indicators to track patterns, changes, and trends of the global climate system.
This plan—an update to the 2009 California Climate Adaptation Strategy—augments previously identified strategies in light of advances in climate science and risk management options.
Intense rainstorms, floods, and heat waves will become more common in the Great Lakes region due to climate change in the coming decades. While ice-cover declines will lengthen the commercial navigation season on the lakes, warmer lake temperatures will increase risks from invasive species, and could threaten water quality. Material in this report is largely a synthesis of the information contained in the National Climate Assessment’s chapters on the Midwest (Chapter 18) and Northeast (Chapter 16). Donald Scavia, GLISA's co-director, was one of the convening authors of the NCA's Midwest regional chapter; GLISA also served as a hub for the compilation of technical inputs for the Midwest chapter.
The National Climate Assessment assesses the science of climate change and its impacts across the United States, now and throughout this century. It documents climate change-related impacts and responses for various sectors and regions, with the goal of better informing public and private decision making at all levels.
The assessment draws from a large body of scientific peer-reviewed research, technical input reports, and other publicly available sources; all sources meet the standards of the Information Quality Act. The report was extensively reviewed by the public and experts, including a panel of the National Academy of Sciences, the 13 federal agencies of the U.S. Global Change Research Program, and the Federal Committee on Environment, Natural Resources, and Sustainability.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Working Group II's contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) relates to climate impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. A Summary for Policymakers and the underlying scientific and technical assessment are also available.
This update serves as guidance for hazard mitigation for the State of Connecticut. Its vision is supported by three central goals, each with an objective, a set of strategies, and associated actions for Connecticut state government, stakeholders, and organizations that will reduce or prevent injury from natural hazards to people, property, infrastructure, and critical state facilities.
This report, the first of its kind for the City of Grand Rapids, outlines the condition of the city's climate resiliency and offers recommendations for how it can both impact and adapt to climate change. The report's goal is to both spur a larger community conversation around processes that will enable Grand Rapids to become a more climate-resilient city and to spur many specific short- and near-term projects, policies, programs, and plans to mitigate the effects of climate change. The report documents projected local climate changes, their potential negative impact to low-income families, and outlines small near-term solutions that the city can make to curb or adapt to climate change. Recommendations include investing in green space and improving the city's tree canopy, improving the city's energy autonomy, and implementing green street infrastructure materials and maintenance techniques.