Access a range of climate-related reports issued by government agencies and scientific organizations. Browse the reports listed below, or filter by scope, content, or focus in the boxes above. To expand your results, click the Clear Filters link.
To become climate resilient requires collective action. Our efforts must take a Whole-of-Government and Whole Community approach.
The Resilient Nation Partnership Network is working to address this through partnership. The result of our collective action is this Building Alliances for Climate Action resource. It is the work of many organizations and individuals, including federal representatives, faith leaders, community-based organizations, mayors and many more. At a time when many are searching for direction on how to address the climate crisis, this resource represents a unifying voice, helping guide the Whole Community forward
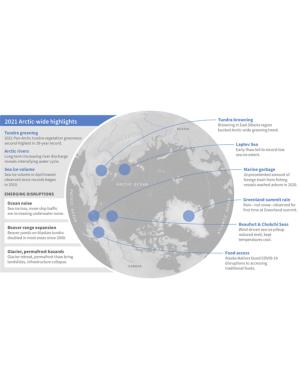
As the influences of human-caused global warming continue to intensify, with the Arctic warming significantly faster than the globe overall, the 2021 Arctic Report Card (ARC2021) brings a broad view of the state of the Arctic climate and environment. The ARC2021 provides an update on seven Arctic Vital Signs, from sea ice to snow and air temperatures to tundra greenness, and checks in on three Indicator topics for updates on river discharge, ocean acidification, and observations of substantial Arctic beaver expansion. The noteworthy emerging topics in the four ARC2021 Frostbites—marine debris, marine noise, food access during the COVID-19 pandemic, and glacier and permafrost hazards—share a common link as they look at the impacts of more people and human activity in the Arctic as well as the challenges and hazards people face with the rapidly changing cryosphere. The scientific and observational story of the Arctic is a human story—of climate change, of increased shipping and industrial activity, and of communities responding to local and regional disruptions.
This is the FY22 edition of the U.S. Gllobal Change Research Program's annual report to Congress mandated by the the Global Change Research Act. The report provides an overview of the Program’s progress in delivering on its strategic goals as well as a summary of agency expenditures under USGCRP’s budget crosscut.
The Working Group II contribution to the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report assesses the impacts of climate change, looking at ecosystems, biodiversity, and human communities at global and regional levels. It also reviews vulnerabilities and the capacities and limits of the natural world and human societies to adapt to climate change.
Drawing and building on the findings of the Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme's (AMAP) 2017 Snow, Water, Ice and Permafrost in the Arctic (SWIPA) assessment, this document provides updated observations, information from other recent assessments, and conclusions from the latest reviews of Arctic trends and indicators. The pace of change in the Arctic is so rapid that new records are being set annually, and each additional year of data strengthens the already compelling evidence of a rapidly changing Arctic.
This Summary for Policymakers summarizes the findings of the AMAP Assessment 2018: Arctic Ocean Acidification report released in October 2018. It offers a review of the latest science relating to regional ocean acidification, the biological responses to it, an overview of case studies and their associated findings, and recommendations for the Arctic Council.
The EWN Atlas is a collection of 56 projects illustrating a diverse portfolio of contexts, motivations, and successful outcomes, presented and considered from an Engineering With Nature® perspective to reveal the usefulness of nature-based approaches and the range of benefits that can be achieved. Engineering With Nature is an initiative of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers enabling more sustainable delivery of economic, social, and environmental benefits associated with water resources infrastructure. EWN intentionally aligns natural and engineering processes to efficiently and sustainably deliver economic, environmental, and social benefits through collaborative processes.
The Second State of the Carbon Cycle Report (SOCCR2) was led and developed by the Carbon Cycle Interagency Working Group under the auspices of the U.S. Global Change Research Program. Contributing to the Fourth National Climate Assessment, SOCCR2 is designed as a special interagency assessment focused on the advances in the science and the understanding of the carbon cycle across North America since the first SOCCR (2007). Specifically, SOCCR2 focuses on U.S. and North American carbon cycle processes, stocks, fluxes, and interactions with global-scale carbon budgets and climate change impacts in managed and unmanaged systems. The report includes an assessment of the carbon stocks and fluxes in soils, water (including near-coastal oceans), vegetation, aquatic-terrestrial interfaces (e.g., coasts, estuaries, wetlands), human settlements, agriculture, and forestry. It considers relevant carbon management science perspectives and science-based tools for supporting and informing decisions. The status of and emerging opportunities for improving measurements, observations, and projections of stocks and fluxes in the carbon cycle, including uncertainty identification, are part of the report.
This special report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate change describes the impacts of global warming of 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels. The report also describes potential global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development, and efforts to eradicate poverty.
The continuing acidification of the Arctic Ocean is projected to have significant ecological and socioeconomic impacts over coming decades, with consequences both for local communities and globally. This is the overarching finding of the 2018 Arctic Ocean Acidification Assessment, presented at the 2018 Arctic Biodiversity Congress. The assessment, conducted by the Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP) of the Arctic Council, updates a 2013 assessment and presents the chemical, biological, and socioeconomic impacts of ocean acidification, which is driven primarily by global greenhouse gas emissions.
This BAMS special report presents assessments of how human-caused climate change may have affected the strength and likelihood of individual extreme events. This sixth edition of explaining extreme events of the previous year (2016) from a climate perspective is the first of these reports to find that some extreme events were not possible in a pre-industrial climate.
This report documents that the average temperature in 2015 was over one degree higher than pre-industrial times and that the period 2011–2015 was the warmest five-year period on record, consistent with established warming trends. The report further documents that in 2015 another milestone was reached, with globally averaged CO2 levels of 400 parts per million (ppm). The year 2016 is on track to be even warmer and will be the first year in which CO2 at the Mauna Loa Observatory remains above 400 ppm all year, and for many generations to come.
The probability of extreme climate events since 2011, especially those involving extreme high temperatures, has been substantially increased by climate change, often by a factor of 10 or more. The single most significant event in humanitarian terms, with over 250,000 lives lost, was the 2011–2012 famine in the Horn of Africa, where drought was a major factor.
As climate changes and ocean temperatures rise, the abundance, distribution, and life cycles of fish in federally managed ocean fisheries may change too. Federal agencies managing ocean fisheries have limited information to determine exactly how climate change might harm specific fish populations, and may not always understand the potential effects. To better manage climate-related risks, the report recommends (1) the development of guidance on how to incorporate climate information into the fisheries management process, and (2) finalizing Regional Action Plans for implementing the NOAA Fisheries Climate Science Strategy that incorporate performance measures for tracking achievement of the Strategy’s Objectives.
A 24-year tradition encompassing the work of 425 authors from 57 countries, 2013's State of the Climate report uses dozens of climate indicators to track patterns, changes, and trends of the global climate system.
This publication, known by the acronym SOFIA, is released every two years to provide policymakers and civil society with a global view of fisheries and aquaculture and associated policy issues. The 2014 report includes a special study of initial assessments of vulnerabilities to climate change in fisheries and aquaculture. The full archive is available online.
Climate change is making the Arctic a greener, warmer, and increasingly accessible place for economic opportunity. However, climate impacts such as sea ice loss and rising ocean acidification are straining coastal community resilience and sound resource stewardship. NOAA's Arctic Action Plan outlines ways for scientists and stakeholders to share their progress regarding this vast, valuable, and vulnerable region.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Working Group II's contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) relates to climate impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. A Summary for Policymakers and the underlying scientific and technical assessment are also available.
This report summarizes the current state of knowledge on potential abrupt changes to the ocean, atmosphere, ecosystems, and high-latitude areas, and identifies key research and monitoring needs. The report calls for action to develop an abrupt change early warning system to help anticipate future abrupt changes and reduce their impacts.
The purpose of this guide—an addendum to regional socioeconomic monitoring guidelines produced by the Global Socioeconomic Monitoring Initiative for Coastal Management (SocMon) and its Pacific counterpart, SEM‐Pasifika—is to provide a minimum set of socioeconomic indicators related to climate change. The aim of these programs is to improve site management of coastal and marine areas by providing simple, user‐friendly guidelines on how to conduct a socioeconomic assessment, which helps coastal managers incorporate community views into adaptive management of marine resources.