Access a range of climate-related reports issued by government agencies and scientific organizations. Browse the reports listed below, or filter by scope, content, or focus in the boxes above. To expand your results, click the Clear Filters link.
This is the FY22 edition of the U.S. Gllobal Change Research Program's annual report to Congress mandated by the the Global Change Research Act. The report provides an overview of the Program’s progress in delivering on its strategic goals as well as a summary of agency expenditures under USGCRP’s budget crosscut.
The Beloved Community is a vision for our future where all people share equally in the wealth and bounty of the earth, where we protect its abundance, diversity, and beauty for future generations. In this vision of liberation, racism, exploitation, and domination are replaced by democracy, cooperation, interdependence, and love. To get there, we pursue transformative, systems-change solutions. What do we mean by this? The root causes of the problems our communities face—like climate change, racism, and economic inequality—are all deeply connected. Since the problems are connected, so are the solutions. The purpose of this toolkit is to put us on the path toward achieving this vision. Through the context of building equity and resilience into climate adaptation planning, we introduce strategies to transform our communities and, by extension, society. Our ultimate goal is to create lasting and systemic change. At the same time, we recognize the urgency of the issues our communities face and the need to take action now. That is why we pursue change at every scale—from policy changes to community-based projects—to institute the transformative change we need to uphold our vision of the beloved community.
The Global Change Research Act of 1990 mandates that the U.S. Global Change Research Program deliver a report to Congress and the President no less than every four years that “1) integrates, evaluates, and interprets the findings of the Program…; 2) analyzes the effects of global change on the natural environment, agriculture, energy production and use, land and water resources, transportation, human health and welfare, human social systems, and biological diversity; and 3) analyzes current trends in global change, both human-induced and natural, and projects major trends for the subsequent 25 to 100 years.” The Fourth National Climate Assessment (NCA4) fulfills that mandate in two volumes. This report, Volume II, draws on the foundational science described in Volume I, the Climate Science Special Report. Volume II focuses on the human welfare, societal, and environmental elements of climate change and variability for 10 regions and 18 national topics, with particular attention paid to observed and projected risks, impacts, consideration of risk reduction, and implications under different mitigation pathways. Where possible, NCA4 Volume II provides examples of actions underway in communities across the United States to reduce the risks associated with climate change, increase resilience, and improve livelihoods. This assessment was written to help inform decision makers, utility and natural resource managers, public health officials, emergency planners, and other stakeholders by providing a thorough examination of the effects of climate change on the United States.
As incomes rise and populations grow, especially in the world’s hotter regions, the use of air conditioners is becoming increasingly common. In fact, the use of air conditioners and electric fans already accounts for about a fifth of the total electricity in buildings around the world–or 10 percent of all global electricity consumption. Over the next three decades, the use of ACs is set to soar, becoming one of the top drivers of global electricity demand. This new analysis by the International Energy Agency shows how new standards can help the world avoid facing such a “cold crunch” by helping improve efficiency while also staying cool.
As a key part of the Fourth National Climate Assessment (NCA4), the U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP) oversaw the production of this stand-alone report of the state of science relating to climate change and its physical impacts. The Climate Science Special Report (CSSR) is designed to be an authoritative assessment of the science of climate change, with a focus on the United States, to serve as the foundation for efforts to assess climate-related risks and inform decision making about responses.
As Volume 1 of NCA4, CSSR serves several purposes, including providing (1) an updated and detailed analysis of the findings of how climate change is affecting weather and climate across the United States; (2) an executive summary and 15 chapters that provide the basis for the discussion of climate science found in the second volume of NCA4; and (3) foundational information and projections for climate change, including extremes, to improve “end-to-end” consistency in sectoral, regional, and resilience analyses within the second volume. CSSR integrates and evaluates the findings on climate science and discusses the uncertainties associated with these findings. It analyzes current trends in climate change, both human-induced and natural, and projects major trends to the end of this century. As an assessment and analysis of the science, CSSR provides important input to the development of other parts of NCA4, and their primary focus on the human welfare, societal, economic and environmental elements of climate change. Much of the underlying report is written at a level more appropriate for a scientific audience, though the Executive Summary is intended to be accessible to a broader audience.
This report focuses on identifying, developing, and implementing strategies to increase the power system’s resilience in the face of events that can cause large-area, long-duration outages: blackouts that extend over multiple service areas and last several days or longer. Resilience is not just about lessening the likelihood that these outages will occur; it is also about limiting the scope and impact of outages when they do occur, restoring power rapidly afterwards, and learning from these experiences to better deal with events in the future.
This Technical Report presents results from a large set of sectoral impact models that quantify and monetize climate change impacts in the U.S., with a primary focus on the contiguous U.S., under moderate and severe future climates. The report summarizes and communicates the results of the second phase of quantitative sectoral impacts analysis under the Climate Change Impacts and Risk Analysis (CIRA) project. The effort is intended to inform the fourth National Climate Assessment (NCA4) of the U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP). The goal of this work is to estimate climate change impacts and economic damages to multiple U.S. sectors (e.g., human health, infrastructure, and water resources) under different scenarios. Though this report does not make policy recommendations, it is designed to inform strategies to enhance resiliency and protect human health, investments, and livelihoods.
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB), in collaboration with the Council of Economic Advisers (CEA), has attempted to quantify the fiscal risks posed by climate change for the Federal Government. To date, this effort has yielded two primary conclusions: first, that our current understanding of the fiscal risks of climate change is nascent, limited in scope, and subject to significant uncertainty; and second, that the evidence available thus far indicates the fiscal risks to the Federal Government could be very significant over the course of this century without ambitious action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) and adapt our communities to a changing climate.
This report outlines the contours of fiscal risk through five program-specific assessments: crop insurance, health care, wildfire suppression, hurricane-related disaster relief, and Federal facility flood risk. These programs were assessed because they are directly influenced by climate change, they have strong links to the Federal Budget, and quantitative scientific and economic models regarding the likely magnitude of impacts were available. This report also considers potential impacts to Federal revenues.
This guide provides basic assistance to electric utilities and other stakeholders in assessing vulnerabilities to climate change and extreme weather and in identifying an appropriate portfolio of resilience solutions. The guide is also part of a broader DOE effort to inform preparedness, resilience planning, and response initiatives.
This document provides final guidance for federal agencies on how to consider the impacts of their actions on global climate change in their National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) reviews, providing a framework for agencies to consider both the effects of a proposed action on climate change, as indicated by its estimated greenhouse gas emissions, and the effects of climate change on a proposed action. The memorandum applies to all types of proposed federal agency actions that are subject to NEPA analysis and guides agencies on how to address the greenhouse gas emissions from federal actions and the effects of climate change on their proposed actions within the existing NEPA regulatory framework.
This report features observed trend data on 37 climate indicators, including U.S and global temperatures, ocean acidity, sea level, river flooding, droughts, and wildfires. It documents rising temperatures, shifting patterns of snow and rainfall, and increasing numbers of extreme climate events, such as heavy rainstorms and record high temperatures. Many of these observed changes are linked to the rising levels of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in our atmosphere, caused by human activities.
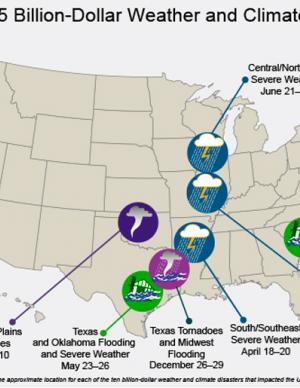
The National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) is the nation's scorekeeper in terms of addressing severe weather and climate events in their historical perspective. As part of its responsibility of monitoring and assessing the climate, NCEI tracks and evaluates climate events in the U.S. and globally that have great economic and societal impacts. Found on these webpages are information on the weather and climate events that have had the greatest economic impact from 1980 to 2015. The U.S. has sustained 188 weather and climate disasters since 1980 where overall damages/costs reached or exceeded $1 billion (including CPI adjustment to 2015). The total cost of these 188 events exceeds $1 trillion.
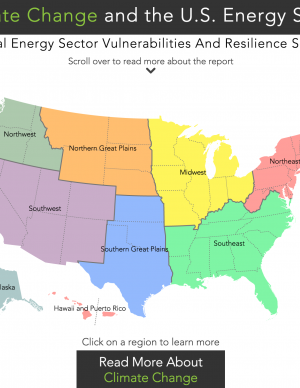
An interactive map provides access to one-page documents of climate and energy information customized for nine regions of the United States. Each document summarizes climate impacts for the region; provides a table of Quick Facts on energy supply and demand, electrical power, and critical infrastructure in the region; and enumerates examples of important energy sector vulnerabilities and climate resilience solutions.
A 24-year tradition encompassing the work of 425 authors from 57 countries, 2013's State of the Climate report uses dozens of climate indicators to track patterns, changes, and trends of the global climate system.
The National Climate Assessment assesses the science of climate change and its impacts across the United States, now and throughout this century. It documents climate change-related impacts and responses for various sectors and regions, with the goal of better informing public and private decision making at all levels.
The assessment draws from a large body of scientific peer-reviewed research, technical input reports, and other publicly available sources; all sources meet the standards of the Information Quality Act. The report was extensively reviewed by the public and experts, including a panel of the National Academy of Sciences, the 13 federal agencies of the U.S. Global Change Research Program, and the Federal Committee on Environment, Natural Resources, and Sustainability.
This report examines current and potential future impacts of climate trends on the U.S. energy sector.
President Obama's Climate Action Plan includes a series of executive actions to reduce carbon pollution, prepare the United States for the impacts of climate change, and lead international efforts to address global climate change.
This Technical Input to the Third National Climate Assessment examines vulnerabilities of infrastructures and urban systems to extreme weather and other events associated with climate change.
This report is the Second National Climate Assessment, summarizing the science and impacts of climate change on the United States. The report discusses climate-related impacts for various societal and environmental sectors and regions across the nation. It is an authoritative scientific report written in plain language, with the goal of better informing public and private decision making at all levels.
This report, a Synthesis and Assessment Product from the U.S. Climate Change Science Program, summarizes the effects of climate change on energy production and use in the United States. It also identifies where research could reduce uncertainties about vulnerabilities, possible effects, and strategies to reduce negative effects and increase adaptive capacity.